You’ve probably heard of the term logistics before; maybe in business news, in a job description or simply when waiting for your online order to arrive. But what exactly is logistics? And why does it matter so much, not just for companies, but also for your everyday life? This guide is written as logistics for starters, making it easy to understand the essentials and avoid mistakes when shipping for the first time.


What is Logistics
Logistics is the process of planning, coordinating and managing the movements of goods from start to finish. It covers everything from transportation to warehousing, inventory management and order fulfillment. Therefore, it’s essential for any business with a supply chain including manufacturers, retailers, healthcare providers, tech companies and even restaurants that need to move their goods from point A to B without having to deal with paperwork and regulations.
With the help of logistics, businesses like yours can reduce cost through efficient storage, transportation and inventory management. At the same time, well-managed logistic services build customer trust by ensuring successful deliveries that leads to higher satisfaction and gives you a real competitive advantage. For logistic starters, knowing these basics makes the process a whole lot easier.
7Rs in Logistics
The 7Rs in logistics represent 7 essential principles for an effective supply chain management. These principles ensure that a business delivers by
- getting the Right product
- in the Right quantity
- in the Right condition
- to the Right place
- at the Right time
- to the Right customer
- at the Right price

Key components in Logistics
To understand how logistics works in practice, it’s helpful to know its key components. The essential parts that keep goods moving efficiently through the supply chain.
Transportation
The first component when talking about logistics is transportation. The process of being transported from one location to another. When you are shipping for the first time, knowing which transport mode suits your product is one of the most important decisions.
Modes of transport
There are four modes of transport that form the backbone of global logistics, as a starter, here’s what you need to know:
| Mode of Transport | Best for | Advantages | Limitations |
| Road Freight | Short distances regional deliveries and last-mile deliveries | Flexible routes, door-to-door service | Less efficient for long distances |
| Ocean Freight | Large volumes of goods in International trade | Most cost-effective for bulk shipments | Slow transit times |
Rail Freight | Heavy or bulk goods over long distances | Reliable, lower costs, eco-friendly | Limited route flexibility |
| Air Freight | High-value, urgent or perishable items | Fastest and most reliable for time-sensitive goods | Highest cost |
Each mode comes with trade-offs, For someone whose shipping for the first time, air freight may look appealing for speed, but road or ocean is more cost-efficient.

Warehousing
Warehousing is used to store goods safely and securely, allowing efficient distribution and delivery.
Types of warehouses
While there are many more types of warehouses – these three types cover most of the logistic needs across industries.
- General Warehouses: A general warehouse acts as a short-term storage space where goods are stored before being delivered to customers. Frequently used by e-commerce and retail supply chains.
- Cold storage: Cold storage warehouses are designed for temperature-sensitive goods that keeps products fresh and safe with refrigeration or freezing. The goods include food, medicine or flowers; and are essential for industries like pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
- Bonded: A secure storage facility used by international companies to keep imported goods before paying duties and taxes. The key benefit is that businesses don’t need to pay immediately when the goods arrive. As soon as the goods leave the warehouse and enter the market, the company is then required to pay the necessary customs duties and taxes.
A recommendation for first time shippers, bonded warehouses are especially useful when importing goods without paying duties immediately.
Types of warehouse services
- Cross-docking: The quick transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transport, reducing the storage time and costs.
- Palletize & Packing: The Palletizing is a service to arrange the goods on a pallet in a stable and space-efficient way. Then the packing is done to prepare individual shipments for storage such as putting them in boxes, crates or protective packaging material.
- Small-docking: The handling of storing small shipments with quick turnaround times.
These warehouse services are common in logistics for starters and vital for companies shipping for the first time.
Inventory Management
Ordering, storing, using and selling a company’s inventory. These include raw materials to finished products, all while providing a warehouse and processing of these items.
Order Fulfillment
An inventory method used to effectively receive, process and deliver goods to customers in a timely manner. The process typically starts when a customer places an order and ends once the order is successfully delivered to them.

What do you need to know to use a logistics service?
When you decide to use a logistics service, it is crucial for you to know your product’s characteristics (size, weight, fragility and the desired destination) and make sure to understand your operational goals like speed and cost and determine if the service can meet your needs for transportation, warehousing, inventory management and order fulfillment.
Be prepared to provide necessary documentation for shipping and ensure that your chosen service has the necessary technology and support. For anyone shipping for the first time, this preparation prevents costly mistakes.
There are several practical details you need to keep in mind when using a logistics service. These include parties involved, preparing the right documents, being aware of the approximate transit times and having a clear idea of the price range. Together, these elements help you plan better, avoid unexpected delays and ensure your goods arrive on time. Let’s go through them:
Parties involved
There are 10 Parties involved in Logistic services:
- Shipper: The company or individual sending the goods
- Receiver: The company or person receiving the goods at the final destination
- Freight Forwarder: The company or an agent that arranges your transport through combining their expertise, connection to trusted suppliers and problem-solving skills.
- Carriers: The company with the vehicles and are the ones who directly carries your cargo from point A to point B.
- Customs Authorities: Customs authorities check documentation, collect duties/taxes and inspect goods.
- Customs Agents: Customs agents Ensure all declarations are correct and duties/taxes are paid.
- Port & Terminal Operators: Operators that manage the loading, unloading and storage at ports and terminals.
- Warehouse Operators: Operators who Manage inventory and prepare goods for the next transport; offering storage, cross-docking, and distribution.
- Insurance Providers: Covers risks (damage, theft or delays) during transport (very important).
- Technology & Finance Partners:
- TMS/WMS providers – digital platforms to plan and track transport and warehousing.
- Coface – A company that will assist you on whether a potential partner is financially stable and reliable before starting a collaboration
- Banks & payment providers – facilitate letters of credit, trade finance and payment security in international trade.
For businesses shipping for the first time, the freight forwarder is often the most important partner – guiding you through customs, carriers and documentation.

Documents needed
- Shipment Details including origin and destination of goods, loading and unloading date and times, specific addresses and contact persons.
- Product Information including quantity (KG), dimensions (LDMs), HS codes and any special handling requirements.
What are LDMs?
LDMs or Loading Meters is the space with which your pallet occupies the truck. The LDMs along with the quantity (KG) and distance (KM) will provide the price to your shipment.
How can you calculate LDMs?
Cargo Length x Cargo Width / 2.4
F.Y.I = A full truck is 13.6 LDMs and has a max. weight of 22 tons (box figo) and 24 tons (tautliner).
When you ship for the first time, understanding LDMs and KG ensures you get an accurate price quote.
- Documentation including all the necessary documentation such as packing lists, T1 documentation or bill of loading; especially for international
Approximate transit times
Transit times in logistics can vary a lot depending on the mode of transport, distance and whether the shipment is direct or consolidated. In regards to road freight transfer times are subject to the drivers plate – if you want to know more about this click here. For a general overview, the approximate transit time in locations worldwide are:
Road Freight
- Domestic (within the same country): 1–3 days
- Regional (e.g. groupage from NL & BE to SP & PT): 2–7 days
- International long-haul (e.g. across Europe): 5–10 days
Ocean Freight
- Short sea shipping (within Europe): 3–7 days
- Intercontinental (e.g. Europe to Asia): 25–40 days
- Europe to the U.S. East Coast: 12-18 days
Rail Freight
- Intra-European: 2–6 days
- China–Europe rail corridor: 14–20 days
- Domestic long-distance (e.g. U.S): 5-10 days
Air Freight
- International express shipments: 1–3 days
- Standard air cargo (airport-to-airport): 3–7 days
- Domestic air shipments: Often same-day or 1-2 days
Price range
Logistics pricing varies widely as it depends heavily on how services are structured and delivered. Some logistic services charge based on weight or volume, while others rely on flat rate or calculate costs by distance traveled. Beyond these factors are options like expedited shipping, cold storage or premium handling which often come with higher rates. On top of that, external influences such as fuel prices, and market demand can cause costs to fluctuate.
*The most regular way to calculate is based on LDM, KG and distance

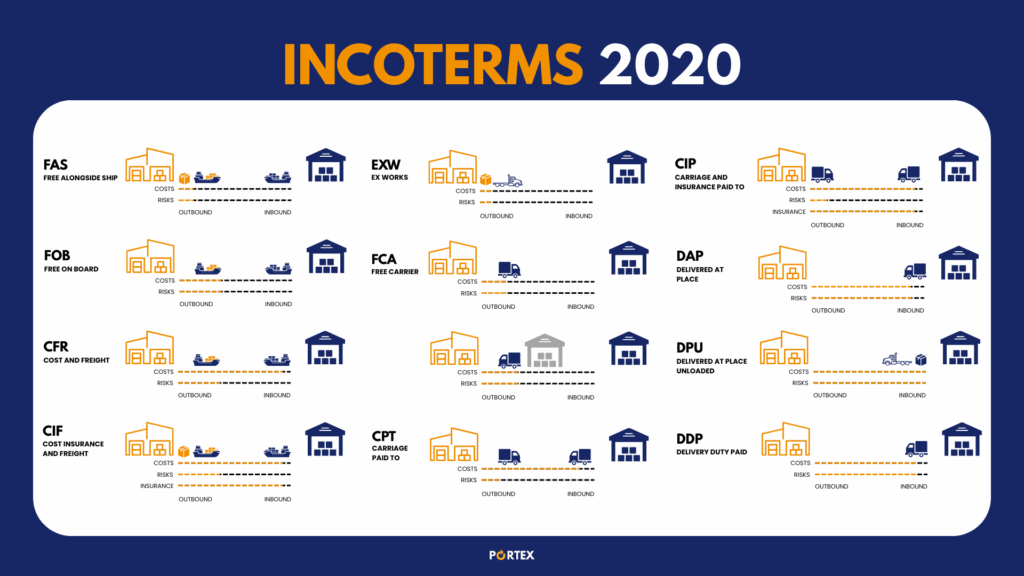
Incoterms®
The Incoterms is a standardized international trade term published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarifies the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in a sales contract. It specifies who pays for and manages the shipment, insurance, documentation, customs and other logistic activities.
Therefore, when organizing an international shipment, it’s important to understand for businesses shipping for the first time that the Incoterms are essential as they tell you exactly when responsibility shifts from seller to buyer.
Conclusion
Logistics is far more than just moving goods from one place to another; It’s the system that keeps global trade and everyday life going. This guide to logistics for starters has covered transportation, warehousing, inventory, documents, transit time and Incoterms. As the industry evolves, digitalization and sustainability will shape the future. For anyone shipping for the first time, understanding these basics ensures smoother operations, fewer delays, and better results.
If you are new to the logistics industry or are looking for a trusted and experienced company to assist your shipping for the first time; you can contact us and we will happily assist you. Portex will handle the process and coordination from start to finish.
